


Diversity for the Amazon
Basin/Region



name Wakaya








Documents


Created to guide the implementation of regional cooperation actions in the area of biological diversity for the next decade, the Regional Program of Biological Diversity for the Basin/Amazon Region of the Amazon Cooperation Treaty Organization (ACTO) adopted the indigenous word Wakaya, of Kokama origin, as its official name. With the meaning of exchange of knowledge, the term Wakaya symbolizes well the cooperation actions necessary to improve the management of biological diversity and the protection of traditional knowledge of indigenous peoples, local communities and other tribal communities of the Basin/Amazon Region, among the eight ACTO Member States – Bolivia, Brazil, Colombia, Ecuador, Guyana, Peru, Suriname and Venezuela.

Program on Biological Diversity for the Amazon Basin/Region
The Regional Program on Biological Diversity for the Amazon Basin/Region is an initiative by the Amazon Cooperation Treaty Organization (ACTO) to inform the implementation of regional cooperation actions related biological diversity. The program will run until 2030, and it supports an improved management of biological diversity and the protection of traditional knowledge of indigenous peoples, local communities and other tribal communities in the Amazon Basin/Region.
The program includes short, medium and long-term collaboration and cooperation actions that support the eight ACTO Member Countries in achieving the commitments under the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD) and the objectives and goals in the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development while recognizing the visions, approaches, models, and instruments implemented by the Member Countries. The program helps strengthen ACTO as a forum for regional exchange and technical and political dialog for the sustainable management of Amazon ecosystems and their biodiversity and ecosystem services.
The Amazon Basin/Region
The Amazon Basin/Region is home to the world’s largest rainforest and an astounding share of unique and irreplaceable biodiversity at the global level. This extraordinary diversity imparts terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems with stability and resilience and is the culmination of complex processes that have been evolving for millions of years.
Geographical Delimitation
As the largest tropical forest in the world and the largest river basin on the planet, the Amazon is hailed as one of the areas with the greatest biological diversity on Earth, home to approximately 10% of the known biological diversity, including elements from 56 ecoregions of internationally relevant ecological systems, 6 natural world heritage sites and more than 10 endemic bird zones.
The region is considered to be the last sanctuary for several endangered species, such as the harpy eagle and the pink dolphin, and is home to a third of the known vascular plants in the world. The Amazon River is the most important source of freshwater in South America and its forests play a strategic role in protecting and controlling the world's climate.
All this wealth is shared by eight ACTO Member Countries: Bolivia, Brazil, Colombia, Ecuador, Guyana, Peru, Suriname, and Venezuela. It covers 44% of South America’s territory, and the continent is home to the largest contiguous tropical forest in the world.

Program Goals
Overall Goal
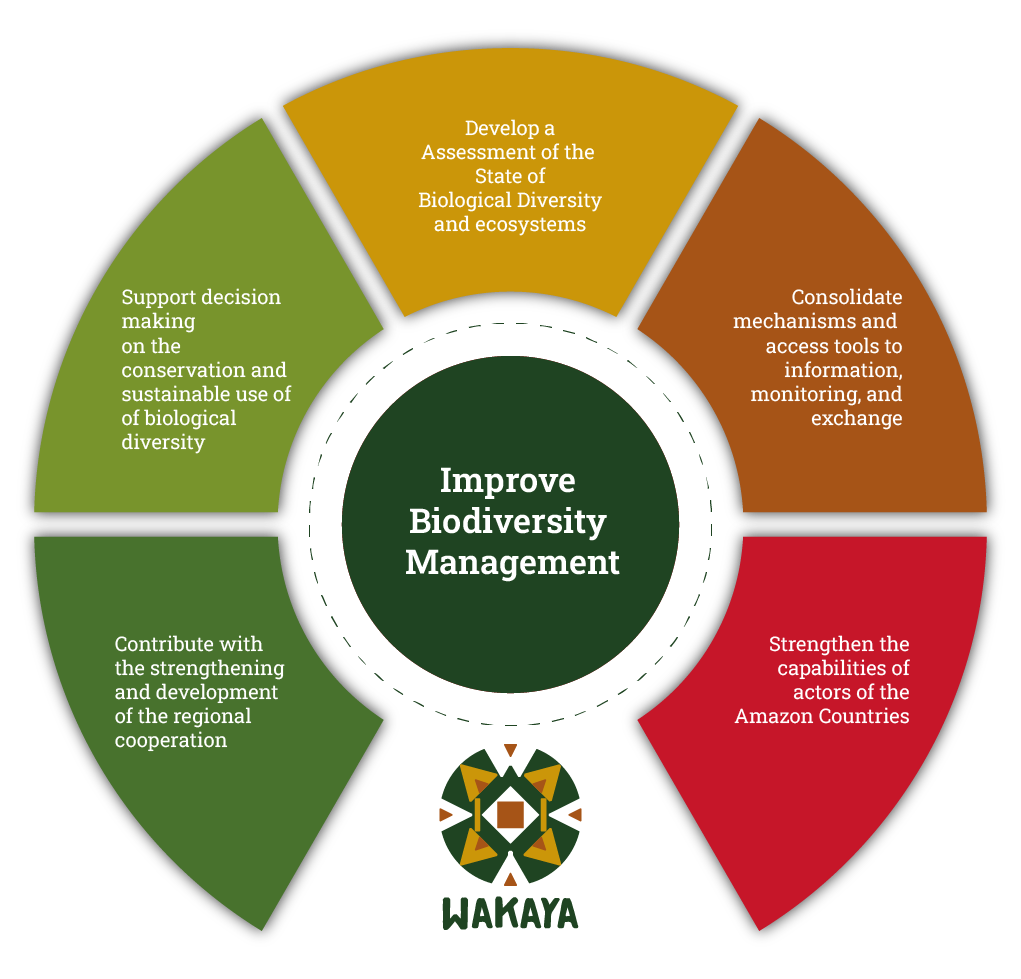
To improve the management of biological diversity and the protection of traditional knowledge of indigenous peoples, local communities and other tribal communities in the Amazon Basin/Region through short, medium and long-term collaborative and cooperative actions in support of the objectives under the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD), its management instruments and the objectives and goals in the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development while recognizing the visions, approaches, models, and instruments implemented by the Member Countries according to their respective regulations.
Discover the components of the Program
1
Scientific analysis of the state of biological diversity and ecosystem services at the regional level
2
Mechanisms and instruments for managing biological diversity
Strengthening the national capacities of the Member Countries
3
4
Strategic planning and institutional strengthening of ACTO
Funding
The implementation of ACTO’s Program on Biological Diversity for the Amazon Basin/Region will be supported through funding from various donors. All contributions, including both regular and ad hoc contributions from Member Countries, and contributions from international cooperation projects and from national public or private companies, will be facilitated by the ACTO Permanent Secretariat (PS), which will provide either support or feedback to the Member Countries during the program implementation stage.
The Regional Program on Biological Diversity for the Amazon Basin/Region will be progressively implemented in accordance with strategic actions planned by ACTO Member Countries. A strategic plan to raise funds will be prepared for the implementation of prioritized regional strategies. According to the plan, fund raising and management for the implementation of the Program will be conducted by the Permanent Secretariat (PS) of ACTO with the support of the Member Countries. The proposal is to put in place a table of donors, as well as coordination with the various aid agencies from the Member Countries and the strategic allies identified for the matter.
News
Documents
Program Partners






Released in may of 2021, the formulation and approval of The Regional Program on the Biological Diversity for the Amazon Basin/Region was launched in May 2021, and it was developed and approved thanks to the commitment and work of the Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Ministry of the Environment and other technical bodies of ACTO’s member countries. In this process, support was provided by the Brazilian Cooperation Agency (ABC) through the Project to Support the Development and Implementation of the Strategic Agenda for Amazon Cooperation and the German Federal Ministry of Economic Cooperation and Development (BMZ), and implementation was conducted by the Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ) GmbH through the Project to Support the ACTO Biodiversity Program under the CBD in Latin America – ACTO Biomaz Project.
